Search
engine optimization (SEO) can encounter various challenges, but here are some of the most common problems and potential solutions to address them:
1.1.
Lack of Keyword Optimization:
Solution:
Conduct thorough keyword research to identify relevant and high-value keywords
for your website. Optimize your content by incorporating these keywords
strategically within your page titles, headings, meta descriptions, and body
text.
To
address the issue of a lack of keyword optimization on your website, follow these
steps to improve your keyword strategy:
1.1.1. Conduct Keyword Research:
Start
by conducting comprehensive keyword research to identify relevant and
high-value keywords related to your business, industry, products, or services.
Use keyword research tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Moz's
Keyword Explorer to find keywords with good search volume and lower
competition.
1.1.2. Focus
on Long-Tail Keywords:
Long-tail
keywords are longer, more specific keyword phrases that target niche audiences.
They often have less competition and can generate more qualified traffic.
Incorporate long-tail keywords into your content strategy to capture specific
user intent and improve relevancy.
1.1.3. Optimize
Page Titles:
Include
your target keywords naturally within your page titles. Craft compelling titles
that accurately describe the content and entice users to click. Place the
keyword closer to the beginning of the title, but ensure it remains readable
and appealing to users.
1.1.4. Optimize
Meta Descriptions:
Write
unique and persuasive meta descriptions that summarize the content of each
page. Incorporate relevant keywords while maintaining a compelling and concise
description that encourages users to click through from the search results.
1.1.5. Enhance
Heading Tags:
Utilize
heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) to structure your content and highlight
important sections. Incorporate keywords naturally within your heading tags to
signal the relevance of the content to search engines and users.
1.1.6. Optimize
Content:
Create
high-quality, valuable content that incorporates your target keywords
naturally. Ensure the content is well-structured, easy to read, and provides
value to your audience. Avoid keyword stuffing, as it can harm your SEO.
Instead, focus on creating informative and engaging content that satisfies user
intent.
1.1.7. Incorporate
Keywords in URLs:
Include
relevant keywords in your page URLs to provide additional context to search
engines and users. Keep the URLs concise, descriptive, and readable. Use
hyphens (-) to separate words for better readability.
1.1.8. Optimize
Image Alt Tags:
Add
descriptive alt tags to your images that include relevant keywords. Alt tags
help search engines understand the content of your images and provide an
opportunity to optimize for relevant keywords.
1.1.9. Monitor
and Refine:
Regularly
monitor the performance of your optimized keywords through analytics tools.
Analyze user behavior, search rankings, and keyword performance to identify
opportunities for improvement. Refine your keyword strategy based on data and
user feedback.
Remember,
keyword optimization should be done naturally and in a user-friendly manner.
Strive to create valuable content that satisfies user intent while
incorporating relevant keywords to enhance your website's visibility and
organic search rankings.
1.2
Poor Website Structure and
Navigation:
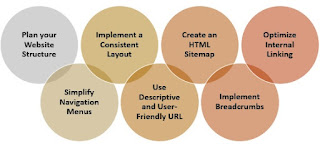
Solution: Ensure your website has a clear and logical structure that allows search engines and users to navigate easily. Create a sitemap, use descriptive URLs, and organize your content into categories or sections. Implement internal linking to connect relevant pages and improve user experience. Improving the structure and navigation of your website is crucial for user experience and search engine optimization. Here's how you can fix a poor website structure and navigation:
1.2.1 Plan
your Website Structure:
Define
a clear and logical hierarchy for your website's pages. Categorize and group
related content together to create a structured framework. Consider using a
mind map or visual diagram to visualize your website's structure before
implementation.
1.2.2 Simplify
Navigation Menus:
Streamline
your navigation menus by reducing the number of menu items and using
descriptive labels. Keep it concise and organized, ensuring that users can
easily find what they're looking for. Use drop-down menus or submenus when
appropriate to display additional navigation options.
1.2.3 Implement
a Consistent Layout:
Maintain
a consistent layout across your website, including headers, footers, and
sidebars. Consistency helps users navigate your site more easily and creates a
cohesive user experience. Place important elements, such as navigation menus,
in predictable locations for better usability.
1.2.4 Use
Descriptive and User-Friendly URLs:
Optimize
your URLs to be descriptive and user-friendly. Incorporate relevant keywords
and make them easy to understand. Avoid using long strings of numbers or
special characters that don't provide meaningful information.
1.2.5 Create
an HTML Sitemap:
Develop
an HTML sitemap page that lists all the important pages of your website. This
provides a hierarchical overview and helps users and search engines navigate
through your content more efficiently. Ensure the sitemap is easily accessible
and linked from your website's footer or navigation menu.
1.2.6 Implement
Breadcrumbs:
Breadcrumbs
are a navigation aid that displays the user's path from the homepage to the
current page. They improve the user experience and provide contextual
information about the page's position within the site's structure. Implement
breadcrumbs to enhance navigation and make it easier for users to backtrack.
1.2.7 Optimize
Internal Linking:
Use
internal links strategically to connect related pages within your website.
Incorporate keyword-rich anchor text to provide context for search engines.
Internal linking improves navigation, distributes link equity, and helps search
engines understand the relationships between your content.
1.2.8 Test
and Improve:
Regularly
test your website's structure and navigation by seeking feedback from users or
conducting usability tests. Analyze user behavior through website analytics to
identify areas of improvement. Make data-driven decisions and iterate on your
website's structure based on user feedback and performance metrics.
1.3
Spam traffic (referral SPAM)
Referral
spam, also known as spam traffic, can be a nuisance as it skews your website
analytics data and provides inaccurate information about your actual website
visitors. Here's how you can address and mitigate spam traffic:
Monitor
your website analytics regularly to identify suspicious or spammy referral
sources. Look for unusual patterns, such as a high number of visits from
unfamiliar domains or sites that don't seem relevant to your industry or
audience.
1.3.2 Set
Up Filters in Google Analytics:
Utilize
Google Analytics filters to exclude spam traffic from your data. Create a
segment or filter that blocks traffic from known spam domains or sources. This
will help you filter out unwanted traffic and ensure more accurate reporting.
1.3.3 Use
Bot and Referral Exclusion Lists:
Take
advantage of the Bot Filtering feature in Google Analytics, which helps
identify and exclude known bots and spiders from your reports. Additionally,
utilize the Referral Exclusion List to exclude certain domains that generate
spammy referrals.
1.3.4 Implement
a CAPTCHA:
Consider
implementing a CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell
Computers and Humans Apart) on your website's forms. This can help reduce spam
bots' ability to access and interact with your site.
1.3.5 Utilize
.htaccess or server configurations:
Add
rules to your website's .htaccess file or server configurations to block or
redirect traffic from known spam domains or suspicious IP addresses. Consult
with a developer or refer to online resources for the correct implementation.
1.3.6 Regularly
Update and Secure Your Website:
Keep
your website's CMS (Content Management System), plugins, and themes up to date
to minimize security vulnerabilities that spammers may exploit. Use strong
passwords and implement security measures like firewalls to prevent
unauthorized access.
1.3.7 Monitor
Traffic Patterns:
Regularly
monitor your website's referral traffic to identify any new spam sources. Stay
updated with industry news and online communities where webmasters share
information about emerging spam tactics.
1.3.8 Educate
Yourself and Stay Informed:
Stay
informed about the latest spam techniques and best practices for combating spam
traffic. Keep up with SEO and webmaster communities, read reputable blogs, and
follow official Google resources to stay ahead of spammers.
By
implementing these strategies, you can minimize the impact of spam traffic on
your website's analytics and ensure more accurate reporting of your actual user
behavior and performance.
1.4
Slow Page Load Speed:
Solution: Optimize your website's performance by minimizing file sizes, compressing images, and leveraging browser caching. Utilize a content delivery network (CDN) to distribute your website's files across multiple servers, reducing load times.
Improving page load
speed is crucial for providing a positive user experience and optimizing your
website for search engines. Here are some steps you can take to fix the issue
of slow page load speed:
1.4.1 Optimize
Image Size and Format:
Compress and resize images
to reduce their file size without compromising quality. Use image compression
tools or plugins to optimize images automatically. Consider using modern image
formats like WebP, which provide better compression compared to traditional
formats like JPEG or PNG.
1.4.2 Enable
Browser Caching:
Leverage browser
caching to store static resources (e.g., images, CSS, JavaScript) on visitors'
devices. This way, returning visitors don't need to re-download these
resources, resulting in faster page loading times. Set cache expiration headers
appropriately to balance freshness and performance.
1.4.3 Minify
CSS, JavaScript, and HTML:
Minify your website's
CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files by removing unnecessary spaces, comments, and
line breaks. Minification reduces file sizes, resulting in faster downloads and
improved page load speed. Use automated tools or plugins to simplify this process.
1.4.4 Enable
GZIP Compression:
Enable GZIP
compression on your web server to compress your website's files before they are
sent to visitors' browsers. GZIP reduces file sizes significantly, resulting in
faster downloads and improved page load speed. Check with your hosting provider
or utilize plugins to enable GZIP compression.
1.4.5 Reduce
Server Response Time:
Optimize your server's
response time by utilizing caching, using a content delivery network (CDN), or
upgrading to a faster hosting provider. Minimize the number of redirects and
database queries to reduce the time it takes for the server to process
requests.
1.4.6 Minimize
HTTP Requests:
Reduce the number of
HTTP requests required to load your web pages. Combine multiple CSS and
JavaScript files into one to reduce the number of separate requests. Use CSS
sprites for small images and consider lazy loading images to load them only
when they come into the viewport.
1.4.7 Implement
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs):
Utilize a CDN to
distribute your website's static content across multiple servers located in
different geographic regions. CDNs cache your website's files closer to your
visitors, resulting in faster load times, especially for users located far from
your server's location.
1.4.8 Prioritize
Above-the-Fold Content:
Optimize the loading
of above-the-fold content, which refers to the portion of the web page that is
visible without scrolling. Ensure critical content and resources required for
initial rendering, such as CSS and JavaScript, are loaded first. Lazy load non-critical
elements to improve perceived load speed.
1.4.9 Monitor
and Test Performance:
Regularly monitor your
website's performance using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or
WebPageTest. These tools provide insights and suggestions to further optimize
your website's load speed. Conduct performance tests and make iterative
improvements based on the results.
Improving page load
speed requires a combination of optimizing file sizes, leveraging caching
mechanisms, reducing server response time, and streamlining the delivery of
resources. By implementing these strategies, you can significantly enhance your
website's load speed, leading to a better user experience and improved SEO
performance.
1.5
Thin or Duplicate Content:
Solution:
Produce high-quality, original content that provides value to your target
audience. Avoid duplicating content within your website or copying from other
sources. Focus on creating unique and engaging content that addresses users'
search intent.
Fixing the issue of
thin or duplicate content on your website is crucial for search engine
optimization and user experience. Here are steps to address this problem:
1.5.1 Conduct
Content Audit:
Perform a thorough
content audit to identify thin or duplicate content on your website. Use tools
like Google Analytics, Screaming Frog, or manual inspection to assess the
quality and uniqueness of your content.
1.5.2 Remove
or Consolidate Thin Content:
Remove or update thin
content pages that provide little value to users or search engines. Combine
thin content pages with similar topics into comprehensive, in-depth articles.
Redirect or 301-redirect any removed pages to relevant, consolidated content to
preserve link equity.
1.5.3 Rewrite
and Expand Content:
Rewrite and expand
thin content to provide more detailed and valuable information to users.
Conduct additional research, incorporate new insights, and address user needs
more comprehensively. Aim for content that is unique, engaging, and covers the
topic in-depth.
1.5.4 Remove
Duplicate Content:
Identify and remove
any duplicate content from your website. Duplicate content can be problematic
for SEO. Use canonical tags to indicate the preferred version of a page when
you have similar content across multiple URLs. Implement 301 redirects from
duplicate URLs to the canonical version.
1.5.5 Create
Unique Meta Tags:
Ensure each page has a
unique meta title and meta description that accurately represent the content.
Avoid duplicating meta tags across multiple pages, as this can confuse search
engines and users.
1.5.6 Implement
Structured Data Markup:
Incorporate structured
data markup, such as Schema.org, to provide additional context and information
to search engines about your content. Structured data helps search engines understand
the purpose and nature of your content, potentially improving visibility and
relevancy in search results.
1.5.7 Encourage
User-Generated Content:
Foster user-generated
content, such as reviews, comments, or discussions, to add unique and valuable
content to your website. User-generated content can enhance engagement, provide
fresh perspectives, and increase the amount of unique content on your site.
1.5.8 Monitor
Content Regularly:
Continuously monitor
your website for thin or duplicate content. Regularly review new content before
publishing to ensure it meets quality standards and adds value. Set up alerts
or use website auditing tools to identify any new instances of thin or
duplicate content.
Remember, quality and
originality are essential for your website's success. By focusing on creating
unique, valuable, and comprehensive content, you can enhance user engagement,
improve search engine visibility, and provide a better experience for your
audience.
1.6
Inadequate Backlinks:
Solution:
Develop a strong backlink profile by acquiring high-quality backlinks from
reputable and relevant websites. Create valuable content that others will want
to link to naturally. Outreach to industry influencers or engage in guest
blogging opportunities to increase your backlink count.
Addressing the issue
of inadequate backlinks is essential for improving your website's authority and
search engine rankings. Here's how you can fix this problem:
1.6.1 Conduct
a Backlink Analysis:
Start by conducting a
comprehensive backlink analysis using tools like Ahrefs, Moz, or SEMrush.
Identify the quantity and quality of your current backlinks, as well as the
sources from which they originate.
1.6.2 Identify
Relevant and Authoritative Websites:
Identify websites
within your industry or niche that have high authority and a strong online
presence. Look for opportunities to acquire backlinks from these websites, as
they can significantly impact your own site's authority.
1.6.3 Create
High-Quality Content:
Develop high-quality,
valuable content that naturally attracts backlinks. Craft informative blog
posts, in-depth articles, infographics, or videos that are unique and
shareable. When you create exceptional content, other websites are more likely
to link to it as a valuable resource.
1.6.4 Guest
Blogging and Outreach:
Reach out to relevant
websites and offer to write guest posts or contribute articles. Guest blogging
allows you to showcase your expertise, gain exposure, and acquire backlinks
from authoritative sources. Ensure that the content you provide is valuable and
aligns with the host website's audience.
1.6.5 Build
Relationships and Networking:
Engage with
influencers, bloggers, and industry experts in your niche. Build relationships
by participating in discussions, offering insights, and providing value. When
you establish genuine connections, they may link to your content or mention
your website in their own articles.
1.6.6 Leverage
social media and Online Communities:
Actively participate
in relevant social media platforms and online communities. Share your content,
engage with others, and establish yourself as an authority. By building a
strong presence, you can attract attention and acquire backlinks from
individuals and communities interested in your niche.
1.6.7 Fix
Broken Links and Reclaim Mentions:
Use backlink analysis
tools to identify broken links pointing to your website. Reach out to the
website owners and request that they update the broken links with the correct
URLs. Additionally, monitor mentions of your brand or website and reach out to
those who mention you but haven't linked to your site, politely asking for a
backlink.
1.6.8 Monitor
Competitors:
Analyze the backlink
profiles of your competitors to identify potential link-building opportunities.
Look for websites that link to your competitors but not to your site. Develop
strategies to reach out to those websites and demonstrate why linking to your
content would benefit their audience.
1.6.9 Foster
Natural Link Building:
Focus on creating
exceptional content, optimizing user experience, and delivering value to your
audience. When your website offers valuable resources, others are more likely
to naturally link to it. Encourage social sharing and make it easy for users to
share your content, increasing the chances of acquiring organic backlinks.
1.6.10
Monitor and Track Progress:
Regularly monitor your
backlink profile and track the progress of your link-building efforts. Use
backlink analysis tools to identify new backlinks, track their quality, and
ensure that they are helping improve your website's authority and rankings.
Building a strong
backlink profile takes time and effort. It requires a proactive approach to
outreach, content creation, and relationship-building. By implementing these
strategies consistently, you can attract high-quality backlinks and improve the
overall authority and visibility of your website.
1.7
Ineffective Title Tags and Meta
Descriptions:
Solution:
Craft compelling title tags and meta descriptions that accurately represent
your content and entice users to click. Include relevant keywords naturally and
maintain a concise and engaging tone. Optimize meta tags individually for each
page to increase their impact.
Fixing ineffective
title tags and meta descriptions is crucial for improving click-through rates
and optimizing your website for search engines. Here's how you can address this
problem:
1.7.1 Conduct
a Title Tag and Meta Description Audit:
Review your current
title tags and meta descriptions to identify areas that need improvement.
Ensure that each page has a unique and descriptive title tag and meta
description that accurately represent the content.
1.7.2 Use
Relevant Keywords:
Incorporate relevant
keywords naturally into your title tags and meta descriptions. Research and
identify keywords that align with the page's content and user search intent.
However, avoid keyword stuffing, as it can harm your SEO. Focus on creating
compelling, readable, and concise text.
1.7.3 Make
Titles and Descriptions Compelling:
Craft engaging and
compelling title tags and meta descriptions that entice users to click through
to your website. Clearly communicate the value and relevance of your content,
and consider incorporating a call-to-action to encourage users to take the
desired action.
1.7.4 Optimize
Length:
Follow best practices
for title tag and meta description length. Aim for title tags that are around
50-60 characters and meta descriptions that are around 150-160 characters.
Ensure that the most important information is included within the recommended
length to avoid truncation in search engine results.
1.7.5 Reflect
Page Content Accurately:
Ensure that your title
tags and meta descriptions accurately reflect the content of the respective
pages. Misleading or irrelevant titles and descriptions can lead to higher
bounce rates and a negative user experience.
1.7.6 Test
and Refine:
Create multiple variations
of title tags and meta descriptions for your key pages, and test their
performance. Monitor click-through rates and user engagement metrics to
identify which versions are more effective. Refine and iterate based on the
results to optimize your click-through rates.
1.7.7 Incorporate
Unique Selling Points:
Highlight unique
selling points or key differentiators in your meta descriptions to make your
content stand out. Emphasize what sets your page apart from competitors and why
users should choose to click on your listing.
1.7.8 Implement
Structured Data Markup:
Utilize structured
data markup, such as Schema.org, to provide additional context and information
to search engines. Rich snippets generated from structured data can enhance the
appearance of your search listings and attract more clicks.
1.7.9 Regularly
Monitor and Update:
Continuously monitor
the performance of your title tags and meta descriptions using web analytics
tools. Analyze click-through rates, organic traffic, and user engagement to
identify areas for improvement. Regularly update and optimize your title tags
and meta descriptions based on data-driven insights.
Remember, effective
title tags and meta descriptions play a significant role in attracting users to
click through to your website. By optimizing them to accurately represent your
content and make it compelling for users, you can improve click-through rates,
increase organic traffic, and enhance the overall performance of your website.
1.8
Absence of Mobile
Optimization:
Solution:
Ensure your website is mobile-friendly by using a responsive design that adapts
to different screen sizes. Optimize images, utilize mobile-friendly fonts, and
prioritize user experience on mobile devices. Test your website's mobile
performance using Google's Mobile-Friendly Test.
Fixing the absence of
mobile optimization is crucial for providing a seamless user experience on
mobile devices and improving your website's visibility in mobile search
results. Here's how you can address this problem:
1.8.1 Adopt
a Responsive Design:
Implement a responsive
design for your website, which automatically adjusts the layout and content
based on the user's screen size. Responsive design ensures that your website is
mobile-friendly and provides an optimal viewing experience across a variety of
devices.
1.8.2 Use
Mobile-Friendly Templates or Themes:
If you're using a
content management system (CMS) or website builder, choose mobile-friendly
templates or themes that are specifically designed for responsive layouts.
These templates are optimized for various screen sizes and offer
mobile-friendly features out of the box.
1.8.3 Optimize
Page Loading Speed for Mobile:
Improve the loading
speed of your website on mobile devices by optimizing image sizes, leveraging
browser caching, and minimizing the use of external scripts and plugins. Mobile
users expect fast loading times, and a slow website can result in high bounce
rates.
1.8.4 Ensure
Readability and Usability on Mobile:
Optimize the
readability of your content on mobile devices by using legible fonts,
appropriate font sizes, and ample spacing between elements. Make sure that
buttons, links, and interactive elements are easy to tap and navigate on
smaller screens.
1.8.5 Condense
and Simplify Navigation:
Simplify your
website's navigation menu for mobile devices. Use collapsible menus,
drop-downs, or hamburger icons to save screen space and allow users to easily
navigate through your site's content.
1.8.6 Optimize
Forms for Mobile:
Make sure that any
forms on your website are optimized for mobile users. Use responsive form
layouts, larger input fields, and streamlined form fields to make it easier for
users to fill out forms on mobile devices.
1.8.7 Improve
Touch-Friendly Elements:
Ensure that all
interactive elements, such as buttons, links, and menus, are designed to be
touch-friendly. Increase their size, provide sufficient spacing between
elements, and avoid placing them too close to each other to prevent accidental
taps.
1.8.8 Test
on Multiple Mobile Devices:
Test your website on a
variety of mobile devices, including smartphones and tablets, to ensure
consistent and optimized performance across different screen sizes and
operating systems. Identify any issues or inconsistencies and address them
accordingly.
1.8.9 Leverage
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP):
Consider implementing
AMP, a framework that creates fast-loading, mobile-optimized versions of your
web pages. AMP can help improve page loading speed and enhance the mobile user
experience, especially for content-heavy websites.
1.8.10 Monitor Mobile Performance and
User Behavior:
Use mobile analytics
tools to monitor your website's performance on mobile devices. Track key
metrics such as mobile traffic, bounce rates, conversion rates, and user
engagement to identify areas for improvement and make data-driven
optimizations.
By implementing mobile
optimization techniques, you can provide a seamless and user-friendly
experience for mobile visitors, improve search engine rankings, and increase
overall user engagement on your website.
1.9 Insufficient Technical SEO:
Solution:
Perform an SEO audit to identify and resolve technical issues that may hinder
your website's visibility. Address factors such as broken links, crawl errors,
improper use of canonical tags, XML sitemap issues, and robots.txt file errors.
Monitor your website's performance using Google Search Console.
Remember
that SEO is an ongoing process, and it requires continuous monitoring,
analysis, and adaptation. Keep up with the latest SEO best practices and
algorithm updates to maintain your website's visibility and rankings.








No comments:
Post a Comment